Notice: There is no legacy documentation available for this item, so you are seeing the current documentation.
When Google (and other search engines) begin to index your site, it’s common for them to pick up many unwanted URLs that come from your RSS feeds.
Google sees these URLs as unique and tries to index them separately. While this doesn’t harm your rankings (Google is smart enough to figure these things out), it does take up the crawl quota allotted to your site and in turn, could cause delays in indexing.
NOTE:
Crawl quota mainly affects sites with lots of URLs. Users with small sites shouldn’t have a crawl quota.
To combat this, we’ve introduced a new Crawl Cleanup feature inside our Advanced Search Appearance settings to allow our users to fine-tune what Google can pick up.
IMPORTANT:
These settings are designed for advanced users who understand the possible ramifications these changes can make. If you are in any doubt about these settings, please reach out to our Support team.
In This Article
Disabling RSS Feeds Tutorial Video
Check out our video on How to Disable RSS Feeds in WordPress below:
Enabling Crawl Cleanup
To enable the Crawl Cleanup settings, click on Search Appearance in the All in One SEO menu and then click on the Advanced tab.
Scroll down to the bottom of the page and enable the toggle for Crawl Cleanup.
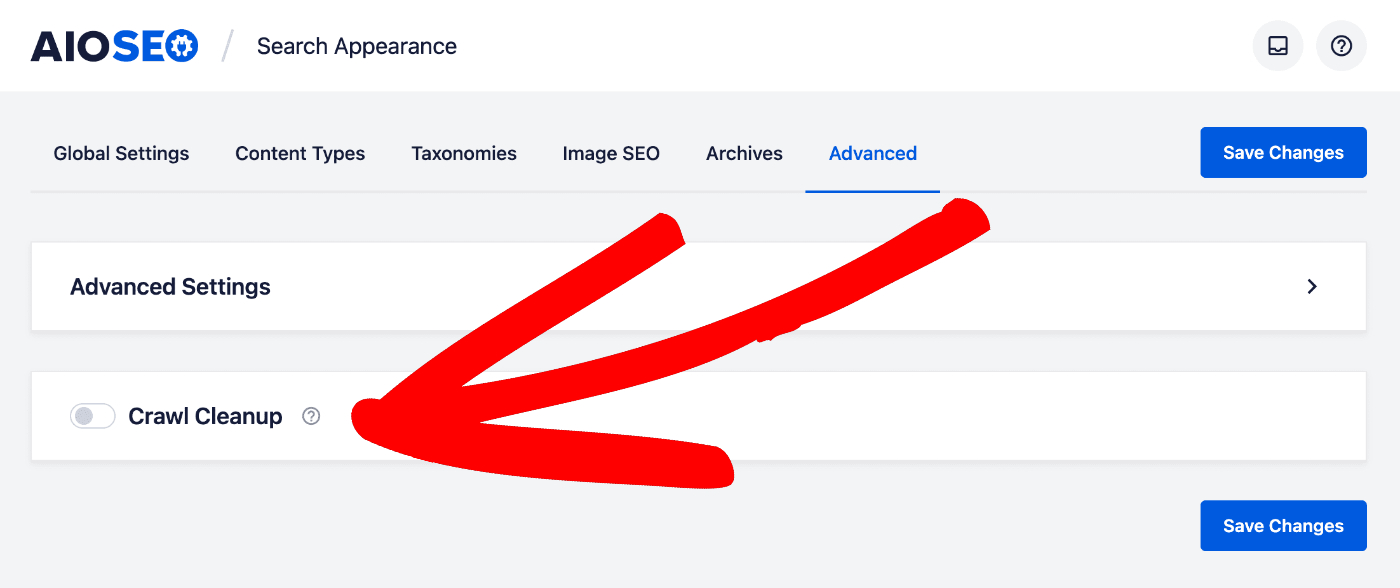
Once enabled, you’ll be presented with quite a few new options for managing your RSS feeds.
RSS Feeds
WordPress includes many RSS feeds on your site, including feeds that are not necessary at all. If you enable Crawl Cleanup, we automatically disable most feeds, keeping your main site feed and some additional feeds that are important.
Global RSS Feed
The global RSS feed is how users subscribe to any new content that has been created on your site. This is enabled by default with Crawl Cleanup and we do NOT recommend disabling it.
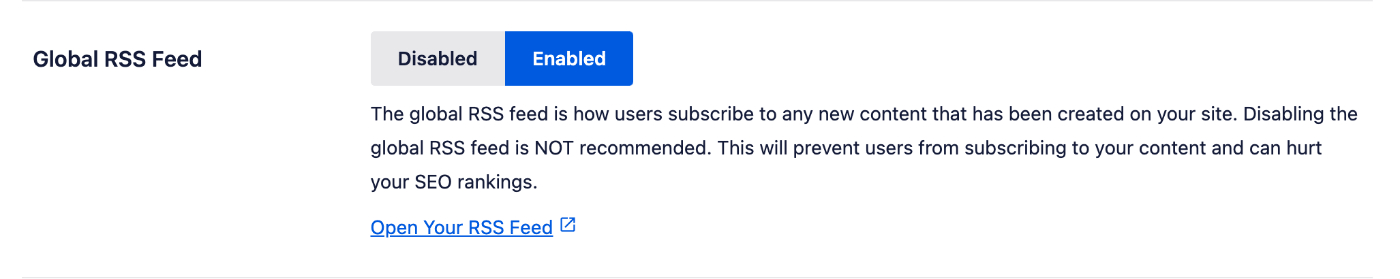
IMPORTANT:
Disabling the Global RSS Feed is NOT recommended. This will prevent users from subscribing to your content and can hurt your SEO rankings.
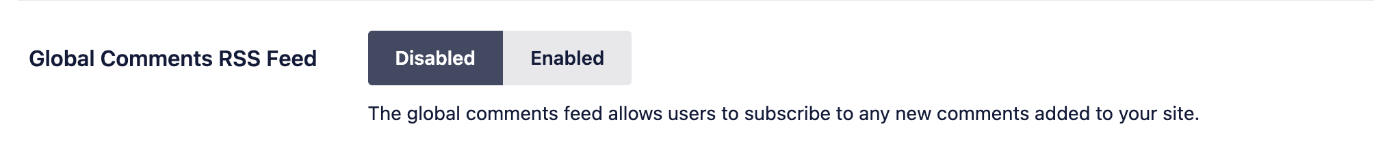
Global Comments RSS Feed
The global comments feed allows users to subscribe to any new comments added to your site. This is disabled by default with Crawl Cleanup.
Static Posts Page Feed
If you are using a static page for your posts (i.e. https://yoursite.com/blog/) Then this option will appear. This is enabled by default with Crawl Cleanup and we do NOT recommend disabling it.
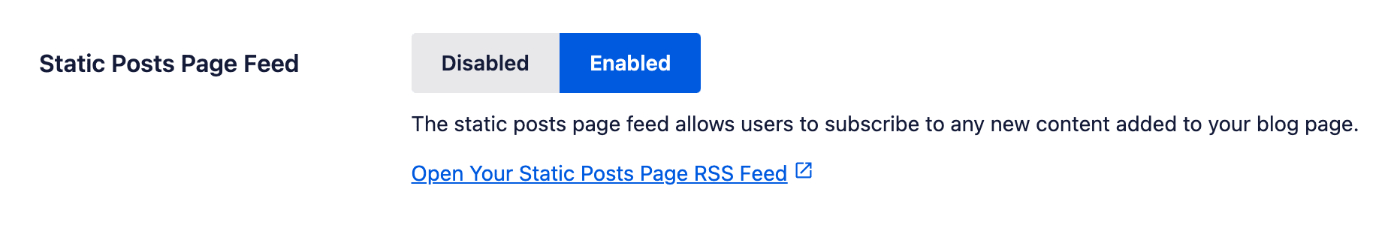
IMPORTANT:
Disabling the Static Posts Page Feed is NOT recommended. This will prevent users from subscribing to your content and can hurt your SEO rankings.
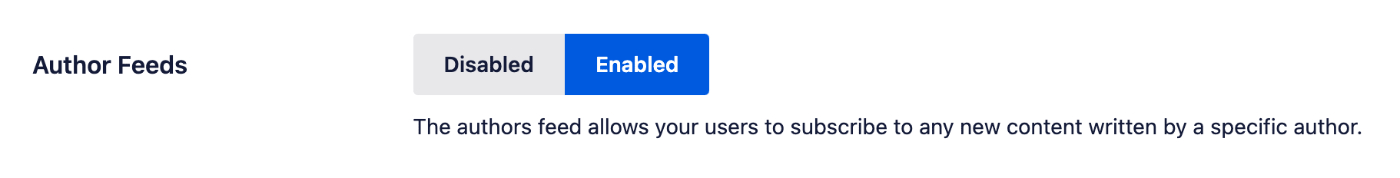
Author Feeds
The authors feed allows your users to subscribe to any new content written by a specific author. This is enabled by default with Crawl Cleanup.
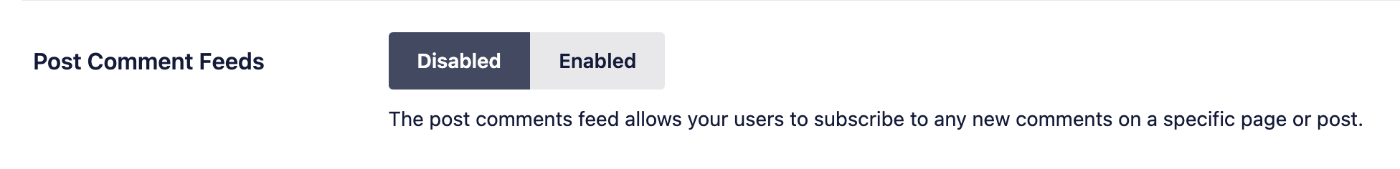
Post Comment Feeds
The post comments feed allows your users to subscribe to any new comments on a specific page or post. This is disabled by default with Crawl Cleanup.
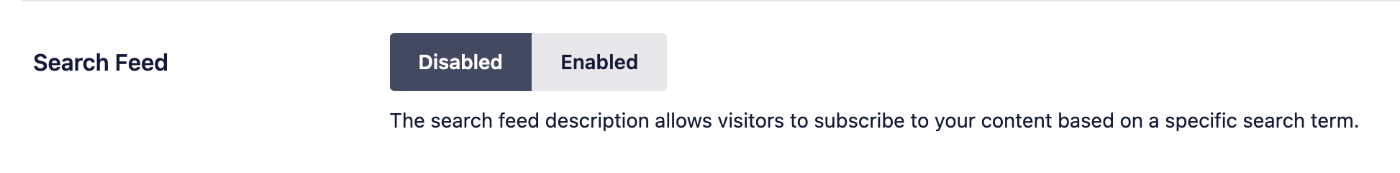
Search Feed
The search feed allows visitors to subscribe to your content based on a specific search term. This is disabled by default with Crawl Cleanup.
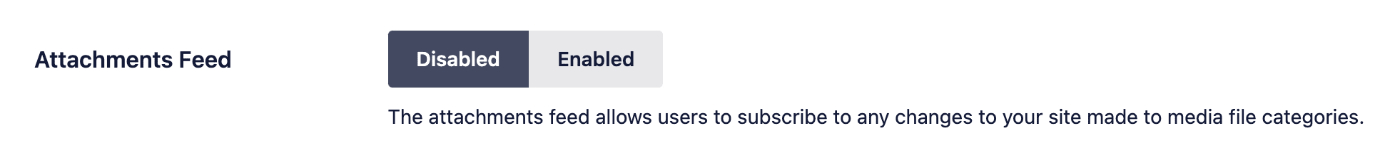
Attachments Feed
The attachments feed allows users to subscribe to any changes to your site made to media file categories. This is disabled by default with Crawl Cleanup.
Paginated RSS Feeds
The paginated RSS feeds are for any posts or pages that are paginated. This is disabled by default with Crawl Cleanup.

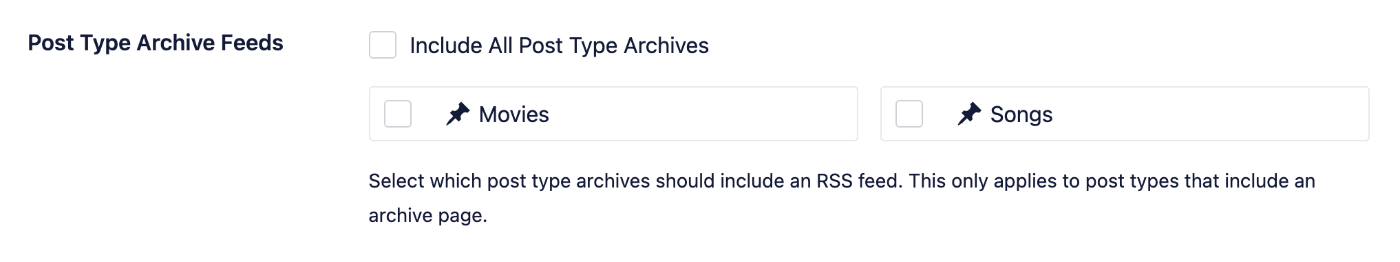
Post Type Archive Feeds
This controls which post type archive feeds are enabled. No post type archive feeds are enabled by default with Crawl Cleanup.
Taxonomy Feeds
This controls which taxonomy feeds are enabled. Only the Categories feed is enabled by default with Crawl Cleanup.

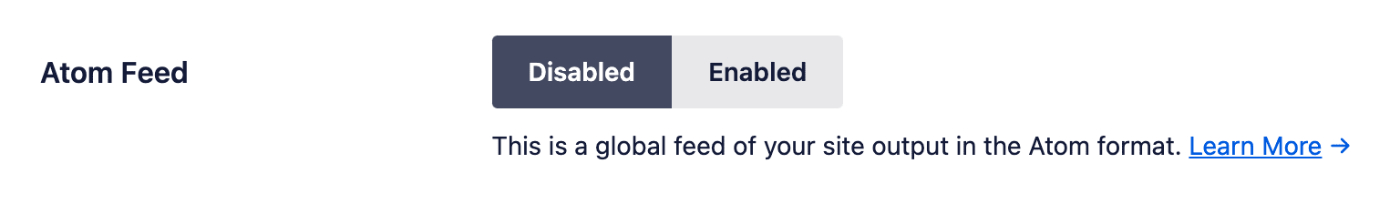
Atom Feed
This is a global feed of your site which is output in the Atom format. This is disabled by default with Crawl Cleanup.
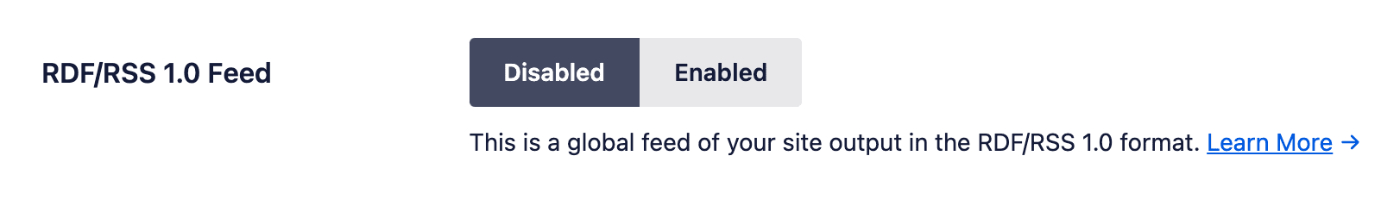
RDF/RSS 1.0 Feed
This is a global feed of your site which is output in the RDF/RSS 1.0 format. This is disabled by default with Crawl Cleanup.
NOTE:
If you select Disabled for any of the feeds detailed above, then the feed will be completely disabled and anyone going to the URL for the feed will be redirected to the homepage or the most relevant archive, i.e. the author archive for author feeds.