Wondering if there’s an optimal word count for SEO? Do longer articles rank better than shorter ones?
Lots of marketers claim that articles need to be long in order to rank. And many promote “ideal” word counts.
In this article, we’ll review those claims and explain what you need to know about word count for SEO.
In This Article
Where Do People Get the Idea that Long Articles Rank Better?
For decades marketers have suggested that articles need to be a certain length in order to rank well in search engine results pages (SERPs).
- Years ago the standard recommended length was 750 words.
- It’s now 1,500 – 2,000 words (minimum).
This idea of word count for SEO spread from news articles and digital marketing blogs.
For example,
- Hubspot reported: “For SEO, the ideal blog post length should be 2,100-2,400 words, according to HubSpot data.”
- Backlinko found that 1,000 – 2,000 words was the optimal word count for attracting social shares, while articles 3,000 words or longer won the most backlinks.
Writers then repeated the idea of an ideal word count for SEO in their own blog posts.
Soon the idea that articles should be at least 2,000 words long was perceived to be a best practice.
However, context was missing.
Taking a Closer Look at Word Count Studies
Hubspot’s ideal length is based on an analysis of their top 50 articles from 2019. (The average word count was 2,300.)
The blog posts they analyzed varied widely in length: from 333 words to 5,581 words. And the median length was 2,164.
- This is a small sample size, from a successful CRM business that writes on niched topics.
- Hubspot did add that 16 of the 50 posts were under 1,500 words. They explained “not all blog posts need to be super long” and “there’s still plenty of opportunity to get your posts ranking even with a lower word count.”
- However, it was the “ideal blog post length” over 2,000 words that got traction on the internet.
With Backlinko’s study, consider that social media signals, like shares, don’t influence Google rankings. So, let’s focus on their observation that articles that are 3,000 words or more get more backlinks.
On the surface this looks like a good argument for chasing high word counts. Like most studies of this type, it’s based on averages and correlation.
This is where things get interesting.
Adding Context and Clarity
SEO data experts Ahrefs have also noted there’s a “strong correlation between word count and backlinks” and “longer content gets more backlinks than shorter content.”
Their analysis of over 900 million pages added important context though: the correlation exists for articles up to 1,000 words.
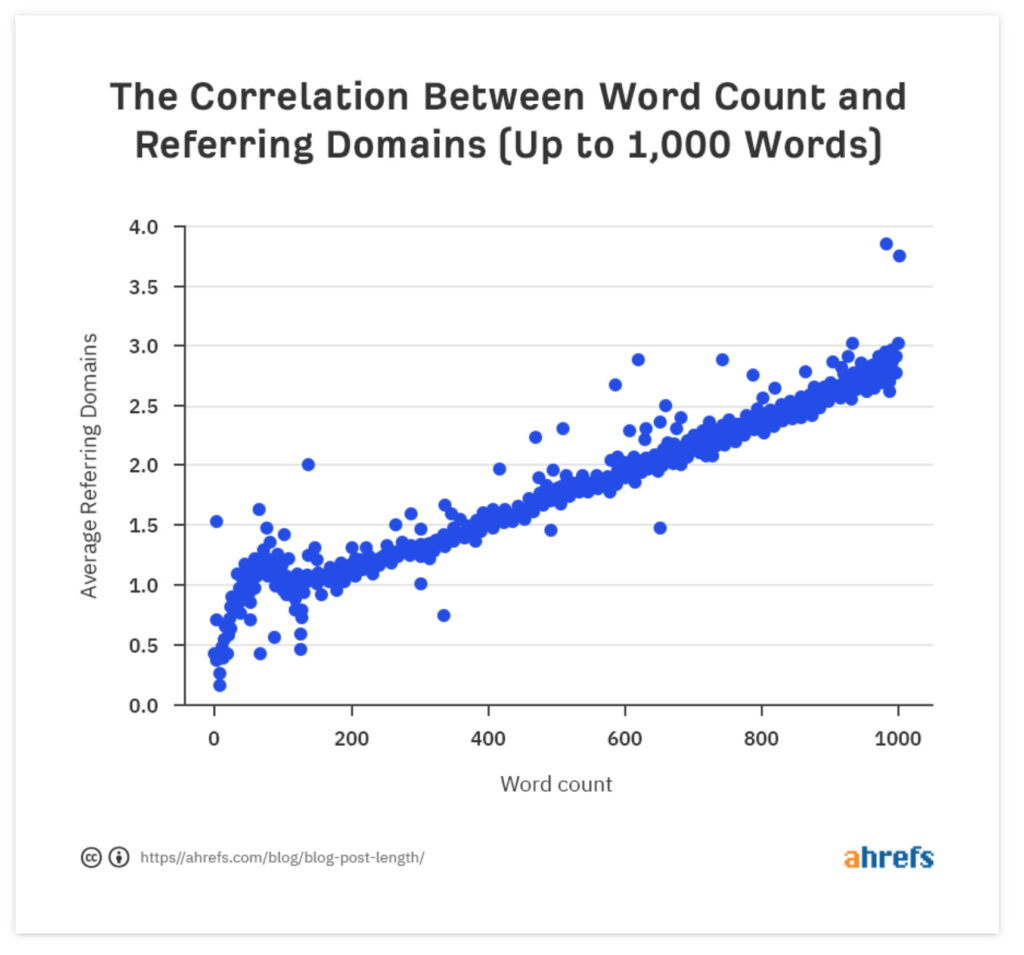
For articles over 1,000 words they found a strong negative correlation.
Ahrefs is a software company that processes billions of pages of data a day to provide SEO professionals with analysis tools.
Joshua Hardwick’s theory that this comes down to “the balance between thoroughness and succinctness” is spot on.
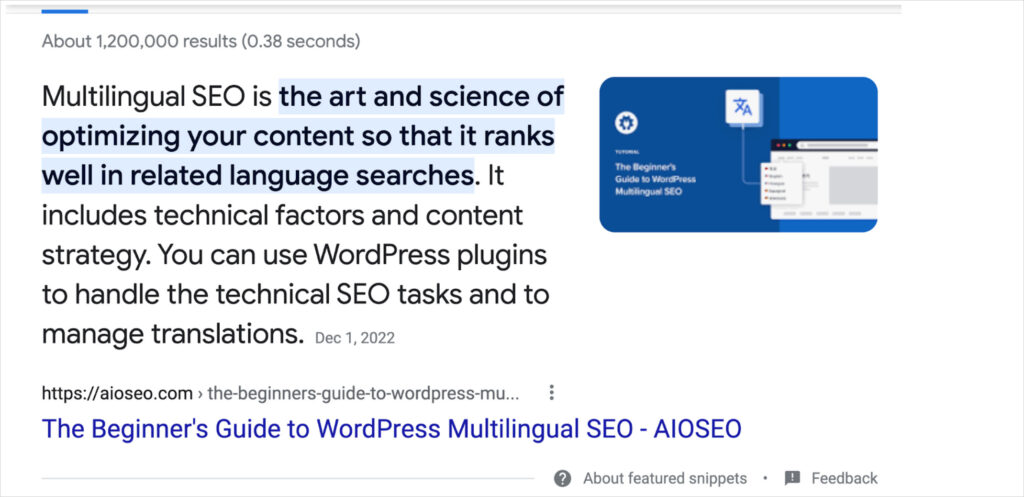
More importantly Google has made it clear that word count has nothing to do with search rankings.
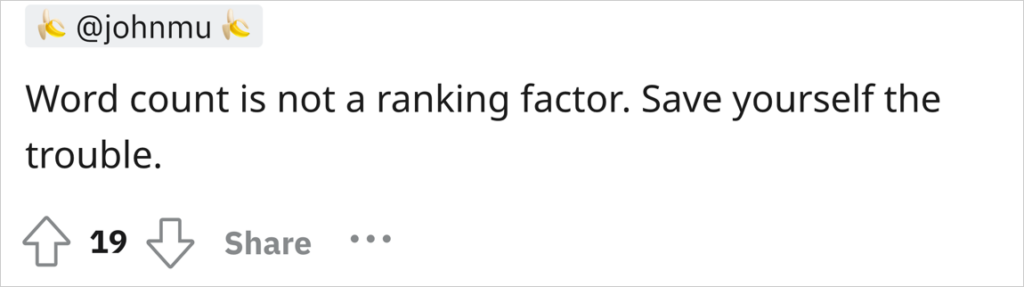
“Word Count is Not a Ranking Factor”
As Google’s John Mueller put it: “Word count is not a ranking factor. Save yourself the trouble.”
This is common sense. After all, if word count was a ranking factor, then “fluff” would win the day. And product pages would be thousands of words long.
So if word count isn’t a ranking factor, what should you focus on? “Awesomeness,” says Mueller.
Indeed, quality is the most important ranking factor for Google’s algorithms. And quality can’t be expressed or defined by word count.
Focus on Creating High-Quality Content
The takeaway is: Focus on creating the best article you can on the keyword (topic) you’ve chosen.
- Write for people, not search engines.
- Organize your article so it’s easy to follow.
- Use plain language.
- Learn how to write for the web.
- Format for scanners.
Review the Competition
Before writing on a topic, review the content currently ranking at the top of search results for that topic.
You will likely find opportunities in this process, like writing an article that’s easier to understand, more succinct, or more accurate.
Explore Long-Tail Keywords
If you want your content to rank higher, consider choosing long-tail keywords as content topics.
Typically, long-tails are easier to rank for and attract quality traffic that converts at a higher rate.
Consider Search Intent
To rank higher, it helps to understand and address search intent in your content. For each keyword, there’s an observable search intent.
You can think of search intent as a sampled mindset of all users. For any given keyword (topic), search intent reveals
- Top questions people have on it.
- Problems they’re trying to solve regarding it.
- Related opportunities they’re seeking.
Use Chrome Incognito to do a search query on a long-tail keyword you’re considering writing on.
What you see on page 1 of search results reveals a wealth of information about search intent.
To the degree that your article helps or satisfies the searcher, you’ll rank well.
On-Page SEO: Optimize Your Web Page
Give yourself every advantage by optimizing your individual web pages.
With the advent of modern content management systems like WordPress and Drupal, many search engine optimization tasks are as easy as filling in a form field and clicking a button.
For WordPress users we recommend the All in One SEO (AIOSEO) plugin.
This is an established plugin with thousands of 5-star reviews on WordPress.
Through a menu that displays inside your WordPress editor, the plugin will make recommendations to improve your web page SEO (also called “on-page SEO“).
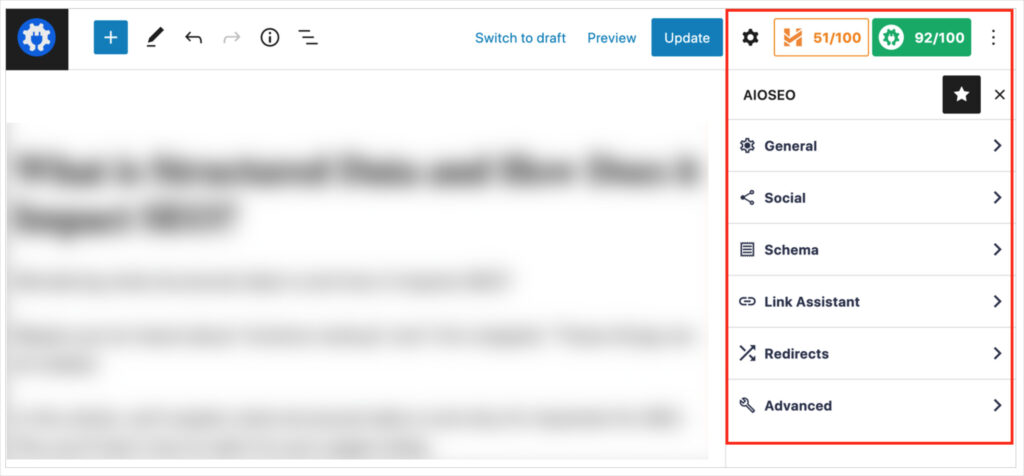
For each piece of content, you’ll see recommendations that include:
- Content structure
- Title tag and meta description
- Image SEO
- Links
- Readability
- Focus keyphrase use
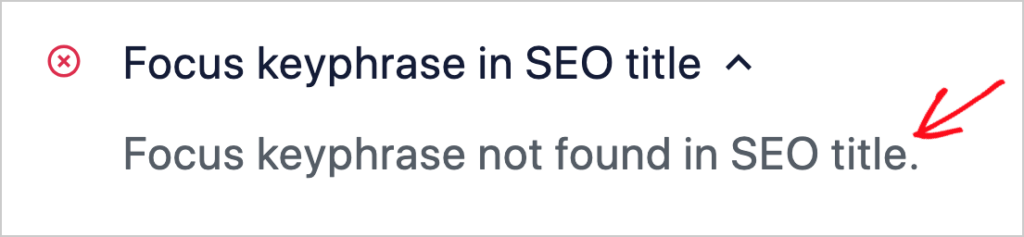
Lastly, making your content eligible to be displayed as a rich snippet in search results is easy with AIOSEO, thanks the click-button interface.
All in One SEO will apply schema markup (a type of code) and that makes your page eligible to be displayed as a rich snippet.
Schema markup helps Google understand your content better, which can result in better or more relevant rankings.
Minimum and Average Word Counts
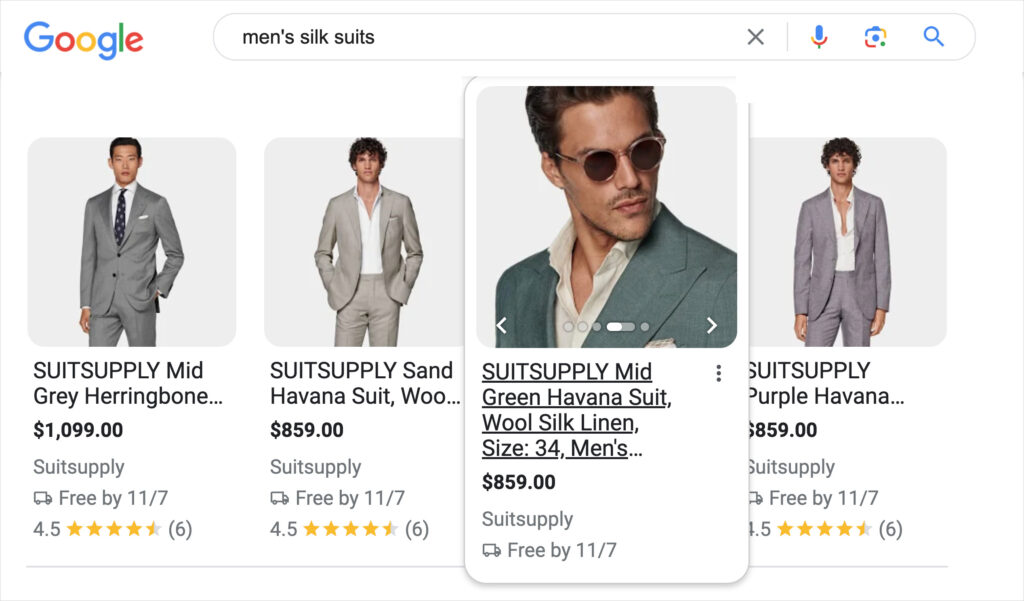
You may have noticed that some marketing tools suggest a minimum word count for different types of posts.
Others, like Clearscope, display a “typical word count” for the topic (keyword) you’re writing on. This “typical word count” is the average word count for top-ranking articles or that keyword.
It’s easy to perceive these recommendations as part of the word count for SEO myth.
But consider: it’s possible that for a given topic you could write an article that’s half the length of top-ranking content, clearer, and more useful.
So it’s best to view these recommendations for what they are: software-generated suggestions. Use your own judgment when it comes to the length of your articles.
While it’s true that longer articles may have a higher chance of ranking for multiple keywords, SEO rankings are dependent on the quality of the article.
Bonus SEO Tips
Once you’re comfortable with on-page SEO, here are some other factors to consider.
- Content strategy: Explore the power of topic clusters.
- Content decay: It’s natural for high-ranking articles to start to slip. Learn how to reverse content decay and regain lost rankings.
- Metrics: Learn how to measure your content performance using free tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console.
- User experience: In its assessment of quality Google also considers user experience. Learn what they measure.
- Conversions: Make the most of your SEO by placing calls-to-action on your pages. Here, a low-cost tool like OptinMonster can help boost conversions and sales.
- Sweat the definition: An excellent definition of a term can go far in helping your article rank and might even land the featured snippet spot.
Summing Up: Word Count for SEO
Your SEO strategy should focus on creating quality content for users. That’s what Google rewards. And the best articles naturally attract backlinks, which can boost rankings further.
While word count isn’t a ranking factor, some topics may require an in-depth treatment.
But comprehensiveness doesn’t necessarily equal quality. Factors like clarity, succinctness, and accuracy are important, and depending on the context, comprehensiveness may not be called for.
Content marketers often refer to in-depth articles as “long-form content.”
The decision on article length needs to be made in the context of the topic, your target audience, the goal of your article, and the top ranking articles you’re hoping to best.
There is no “best word count.” Instead of focusing on the number of words, put your energy into satisfying readers.
What’s Next?
We hope this post helped you understand misconceptions behind word count for SEO. Instead of word count, quality is what consumers — and Google’s algorithms — look for.
Next, explore our article on how to avoid SEO scams and discover the basics of Google search results.
If you found this word count for SEO article helpful, then subscribe to our YouTube Channel. You’ll find plenty of WordPress tutorials there designed for those who want better rankings for their content. You can also follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, or Facebook to stay in the loop.
Disclosure: Our content is reader-supported. This means if you click on some of our links, then we may earn a commission. We only recommend products that we believe will add value to our readers.