What are nofollow, sponsored, or UGC links? And how do they impact SEO?
Understanding these 3 link types can help you get the most out of your SEO efforts.
In this article, you’ll get a simple explanation of nofollow, sponsored, and UGC links. And you’ll find out how to act on this information.
In This Article
Link Building for SEO
Backlinks, or links from other websites to yours, are a significant search engine ranking factor.
Digital marketers create link building campaigns (activities) to increase backlinks to a site.
Campaigns might include:
- Creating and promoting high-quality articles.
- Writing guest articles for other sites in return for a backlink.
Now let’s take a closer look at how links impact SEO.
Link Quality and Attributes
Not all backlinks are equal. Some will have no impact on your rankings. And others can have a positive or negative effect.
The SEO impact of backlinks depends on their quality and attributes.
- Backlinks from high-quality, trustworthy sites can have a positive impact on SEO.
- Backlinks from untrustworthy sites (like financial scam sites) can negatively impact SEO.
- Expect backlinks with nofollow, sponsored, or UGC attributes to have no impact.
Here’s why.
Links from reputable websites can boost your ranking because search engines view these links as endorsements of your site.
But a pattern of backlinks from untrustworthy sites may raise a red flag with Google. Their algorithms may see this pattern as indicating you’re involved in a link scheme. And that can sink your SEO.
And finally, nofollow, sponsored, and UGC links negate the SEO value of link building. That’s why it’s essential to understand what these links are. Otherwise, you could work to build backlinks and get no SEO value from those links.
Now, let’s find out why nofollow, sponsored, or UGC links have no SEO impact.
First, we’ll need a brief explanation of link attributes.
What are Link Attributes?
Link attributes are bits of code that give Google information about a web page’s relationship to a linked page.
These bits of code are contained in the links.
Here are the 3 attributes, what they mean, their SEO value, and what they look like in HTML code.
| Link Attribute | What it tells search engines | Expected SEO value | HTML code |
| nofollow | The linking page doesn’t endorse the page linked to. And search engines should not crawl the page linked to. | None | rel=”nofollow” |
| sponsored | The linking page received money for placing the link. | None | rel=”sponsored” |
| UGC | The linking page is user-generated content. | None | rel=”UGC” |
Now you can see why marketers don’t chase backlinks with any of these attributes: because the links typically don’t provide any bump to search engine rankings.
Keep in mind that any kind of link can provide traffic. If you get a “nofollow” link from the Wall St. Journal, it’s better than no link from them. But a WSJ link without the “nofollow” would be far better.
Link attributes are also called “tags.”
How are Attributes Added to Links?
Before we look at these attributes more closely, let’s see how they’re added to links.
Attributes can be added directly to HTML code for a page, but it’s easier to add them in the website’s editor.
Let’s use WordPress as an example. The All in One SEO (AIOSEO) plugin provides a click-button way to add these attributes to links.
Simply click on any link and you’ll see a pop-up window with toggle buttons.
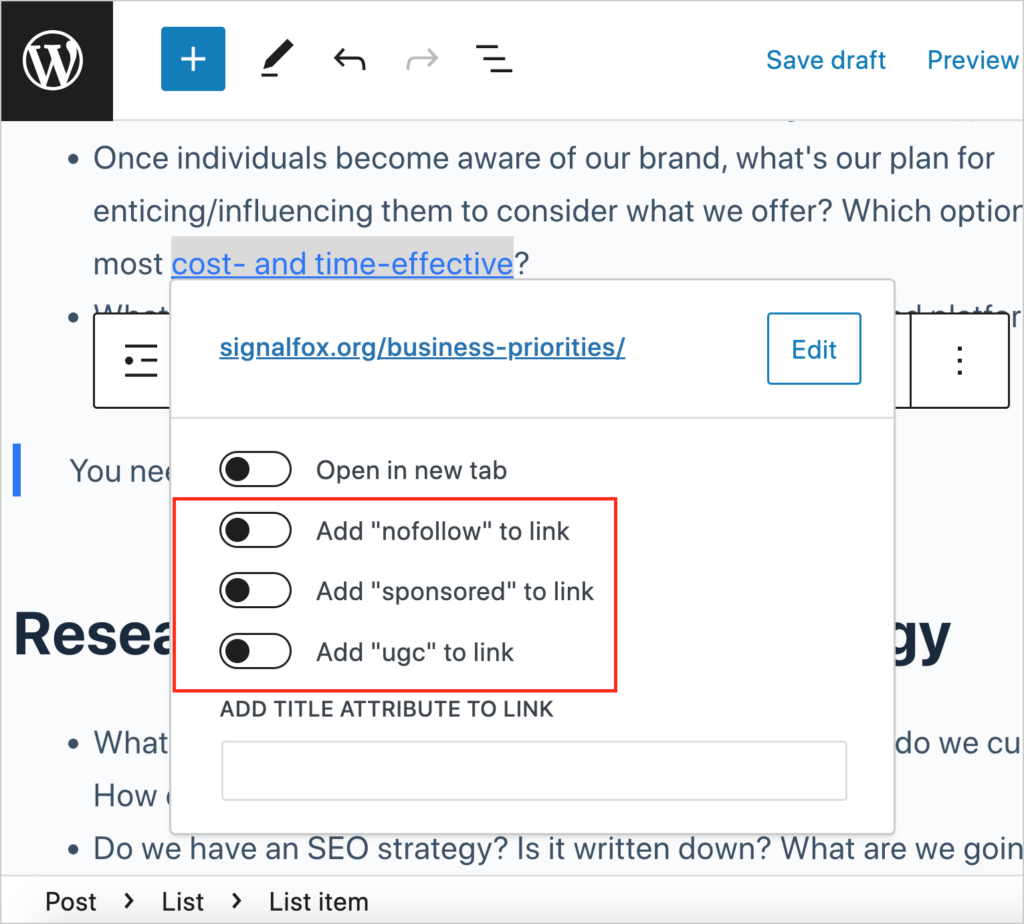
If you toggle on “nofollow,” “sponsored,” or “UGC,” then WordPress will add the related code to the link. You won’t see the code, but it’ll be there.
Link Attributes in HTML
Now, let’s see what the code actually looks like. This will help you understand the differences between the link types.
Here’s what a regular hyperlink looks like in HTML.
<a href="https://example.com">Check out the Example website</a>You’ll notice the link code is on the left and right of the anchor text. (Anchor text is text with a link applied to it.)
Here’s the same link with a nofollow attribute added.
<a href="https://example.com" rel="nofollow">Check out the Example website</a>Here it is with the sponsored attribute:
<a href="https://example.com" rel="sponsored">Check out the Example website</a>And here it is with the UGC attribute.
<a href="https://example.com" rel="ugc">Check out the Example website</a>In addition, links can have more than one attribute.
<a href="https://example.com" rel="nofollow sponsored">Check out the Example website</a>Nofollow Links
We’ve seen how a nofollow link tells search engines that the referring (linking) page does not endorse the linked page.
For this reason, it’s best to check inbound links from guest post campaigns to ensure there’s not a “nofollow” attribute there. (If there is one, ask the site owner to remove it.)
Here’s a bit of nuance, though. Search engines used to treat this attribute as an instruction not to follow (crawl) the link. But in 2020, Google Search began treating nofollow attributes as a hint. Their bots (or “crawlers”) may choose to crawl and index the linked page.
However, given that “nofollow” means “not endorsed,” it’s best not to count on getting any SEO value from such links.
One way that search engines discover new web pages is by crawling links.
Nofollow vs. Dofollow Links
If there’s no SEO value in a nofollow link, what kind of links should you aim to get? Dofollow links.
“Dofollow” is an odd term though. All it means is there isn’t a “nofollow” attribute present.
We can see the difference by looking at the HTML code for a nofollow link.
<a href="https://example.com" rel="nofollow">Check out the Example website</a>Now here’s a dofollow link:
<a href="https://example.com">This is anchor text</a>Did you notice that the “dofollow” link is simply the same as the “regular” hyperlink in our 1st example?
The nofollow attribute is sometimes called the nofollow tag.
Some Practical Reasons Sites Use Nofollow Tags
Large corporations, government entities, universities, and hospitals commonly make all their external links “nofollow.” An exception might be if outbound links go to related subsidiaries or research centers.
Why are these policies used? To avoid the appearance of endorsing an external web page that might seem controversial.
Some site owners may have a plugin or other setting configured to make all external links “nofollow” links. In these cases, they may not be aware that all their external links are marked “nofollow.”
Requesting Removal of a Nofollow Tag
Imagine you wrote a guest article for a site, and their guidelines stipulated you can include a dofollow link to your site. But when the article’s published, you discover there’s a nofollow tag included.
In cases like this, email the site editor and request that the “nofollow tag” or “nofollow attribute” be removed from the link.
What is an easy way to tell whether your inbound links have nofollow tags? Check out our article on How to View Page Source.
Sponsored Links
In the table above, we saw that the sponsored attribute (or “tag”) indicates the linking site has (or may) received financial compensation for the link.
These links may be:
- Backlinks offered in exchange for payment.
- Links provided to guest posters, who paid for their article placement and backlink.
- Affiliate marketing links
- Coupon links
In all these scenarios, the site owner earns money from the links. So it’s not surprising that these links don’t impact SEO.
Remember, search engines will read this “sponsored” tag. So they’ll know you paid for it. And for that reason they won’t view the link as an endorsement of your site.
But what about cases where websites sell links and promise not to add a “sponsored” tag?
These sites typically leave a trail that’s transparent to Google. For instance, they might have a price list posted for links and guest articles.
Paid Links
The bottom line is, using paid links to boost your ranking is against Google guidelines and can result in penalties.
To avoid penalties, use the sponsored attribute where needed.
And if a site editor adds a sponsored tag in error to a guest post backlink, simply ask them to remove it.
UGC Links
UGC stands for “user-generated content.” Examples of user-generated content are forums, comments sections, and sites that allow anyone to post photos or content.
Forum posts are typically low-quality. Therefore, it’s best to exclude them from your content marketing efforts.
While forum site owners may remove the UGC tag for posters that consistently create quality content, the other content will likely be mediocre.
Comments sections typically apply UGC tags automatically to links posted by users. Here, the UGC tag helps in fighting comment spam.
Exceptions
Keep in mind that some niched forums edit and publish high-quality content from experienced professionals.
An example is the TabbForum: a capital markets forum. TabbForum doesn’t add UGC or nofollow attributes to its guest posts.
Attract Links with WordPress SEO
One of the best ways to get backlinks is to attract them by creating and promoting interesting, unique content.
That can lead to a chain reaction of improved search engine rankings, which generate more backlinks.
To get started, ensure you know how to optimize your web pages for SEO.
A plugin like All in One SEO (AIOSEO) simplifies this process. It makes many technical SEO tasks as simple as clicking a button or filling out a form field.
All in One SEO is an established plugin. It has thousands of 5-star reviews on WordPress.org, and over 3 million sites use it.
- You can download it here.
- Follow these instructions to install and activate it.
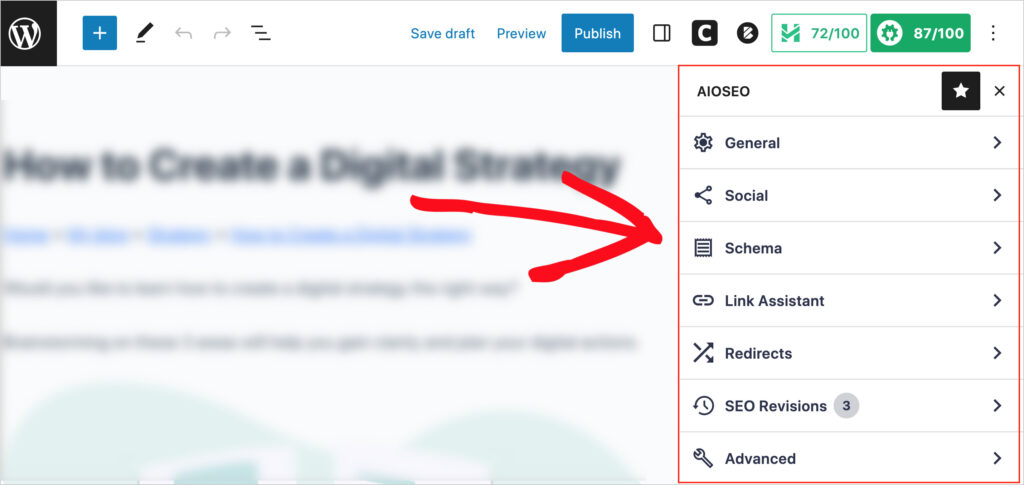
Once you’ve installed All in One SEO (AIOSEO), you can begin optimizing your content.
Navigate to any web page on your site, and the plugin will display simple recommendations for improvement.
Don’t Forget About Internal Links
Ensuring your most important pages (like pricing or product pages) have internal links pointing to them can help Google understand your site and improve the rankings for those pages.
We recommend using All in One SEO’s Link Assistant (available with the Pro version) to simplify this process.
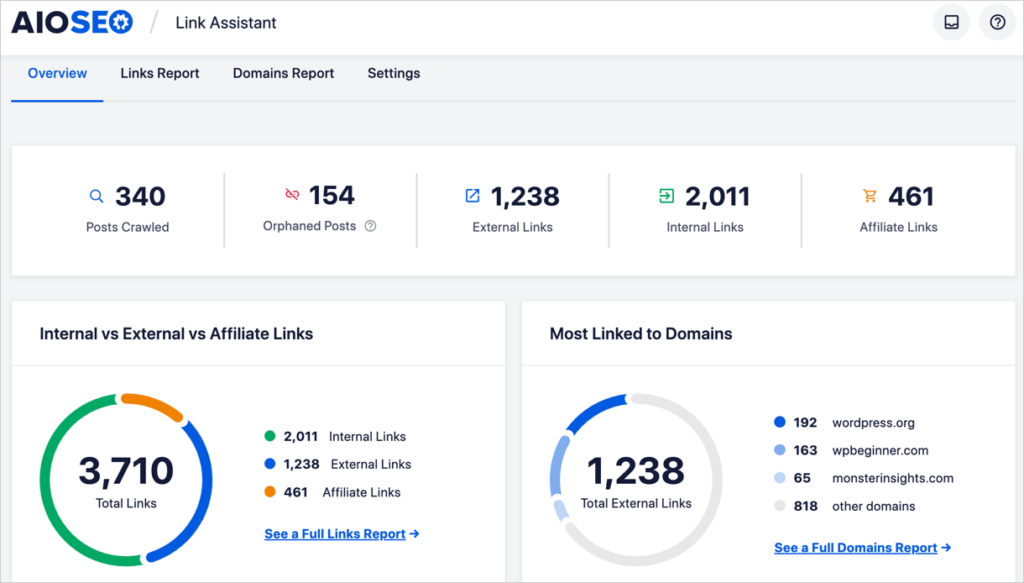
Link Assistant will make recommendations for internal links to add, including which anchor text to place the link on. You won’t need to open the individual pages.
As with all online tools, it’s essential to use your judgment when deciding whether to accept a suggestion.
Bonus tips
- Learn about the role of anchor text in link building and SEO.
- Learn more about the role of quality backlinks in our Link Building Guide.
- Already getting backlinks? Learn how to track traffic in WordPress.
- Make the most of inbound traffic by capturing conversions.
Q&A on Nofollow, Sponsored, and UGC Links
What are good examples of UGC?
UGC stands for user-generated content, and good examples of it include customer testimonials, product or service ratings, and social media content.
While some membership sites allow all users to post articles, this user-generated content is usually low-quality.
Are sponsored links good for SEO?
No, you can’t count on sponsored links boosting your SEO. A sponsored link indicates that you paid for article or link placement. While that action may increase brand awareness and site traffic, sponsored links should not be part of an SEO strategy.
Why use a nofollow link?
Use a nofollow link when you don’t want to pass PageRank to a linked site. The nofollow attribute is the appropriate choice when the UGC or sponsored attributes don’t apply.
Resources On Links
- How to Find and Fix Broken Links in WordPress
- What Are Paid Links in SEO and Do They Work?
- Referring Domains vs. Backlinks: What’s the Difference? (Plus: SEO Impact)
- 6 Ways Link Assistant Can Save You Time on Internal Link Building
- The Ultimate Link Building Guide
- How to Create Jump Links in WordPress
- Nofollow Links vs Dofollow Links: Everything You Need to Know
- Breadcrumb SEO: What Are Breadcrumbs and How Do They Affect SEO?
- 29 Link Building Statistics to Help Power Your SEO Strategy
What’s Next?
We hope this post helped you understand what nofollow, sponsored, and UGC links are and why they typically don’t boost SEO.
You can also check out small business SEO scams and discover the fascinating connection between revenue and backlinks.
If you found this article helpful, please subscribe to our YouTube Channel. You’ll find plenty of search engine optimization tutorials there. You can also follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, or Facebook to stay in the loop.
Disclosure: Our content is reader-supported. This means if you click on some of our links, then we may earn a commission. We only recommend products that we believe will add value to our readers.